Introduction – Yarn Market:
The yarn market has a big impact on Asia’s textile and clothing industries. Meanwhile, the yarn industry is one of the most dynamic parts of the global textile value chain. This sector is shifting trends too fast in raw material costs, demand patterns and trade rules. It also produces sustainability aspirations in this field.
As we know, the textile industry is a major part of Pakistan’s economy. In order to stay competitive in this fast-changing environment this industry has gone through major changes in recent years. Pakistan is changing to address both home obstacles and worldwide possibilities in the yarn business. For example, it is modernising spinning factories and expanding its exports.
Global Overview of the Yarn Market:
China, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Vietnam are the five biggest countries that make up the enormous and diverse yarn market in Asia. Together, these countries manufacture almost 70% of the world’s yarn and are the principal suppliers to the textile and clothing industries across the world.
There are a lot of worldwide elements that are having an effect on the market in 2025:
- Prices of Cotton Going Up and Down: Changes in the weather, trade restrictions, and output have all made the price of cotton move up and down, which has affected spinning margins.
- Rising Synthetic Yarn Demand: There is more and more demand for synthetic yarn. Polyester and blended yarns are becoming increasingly popular, especially in the apparel business, because they are inexpensive and endure a long time.
- Sustainability Pressures: Many Asian mills are investing in modern technology in order to makes yarn in a unique way. This initiative is good for the environment too because eco-conscious customers want organic and recycled fibres.
- Changes in geopolitics: Trade wars, changes in tariffs, and changes in supply chains are changing where important importing areas like Europe and North America get their goods.
These changes throughout the world effect everyone, but Pakistan’s yarn market is at a crucial point when it has to find a balance between export potential and home strength.
Please visit Zarea at this time to view the biomass products and building materials, as well as to check the prices and make a volume purchase.
Pakistan’s Position in the Asian Yarn Market:
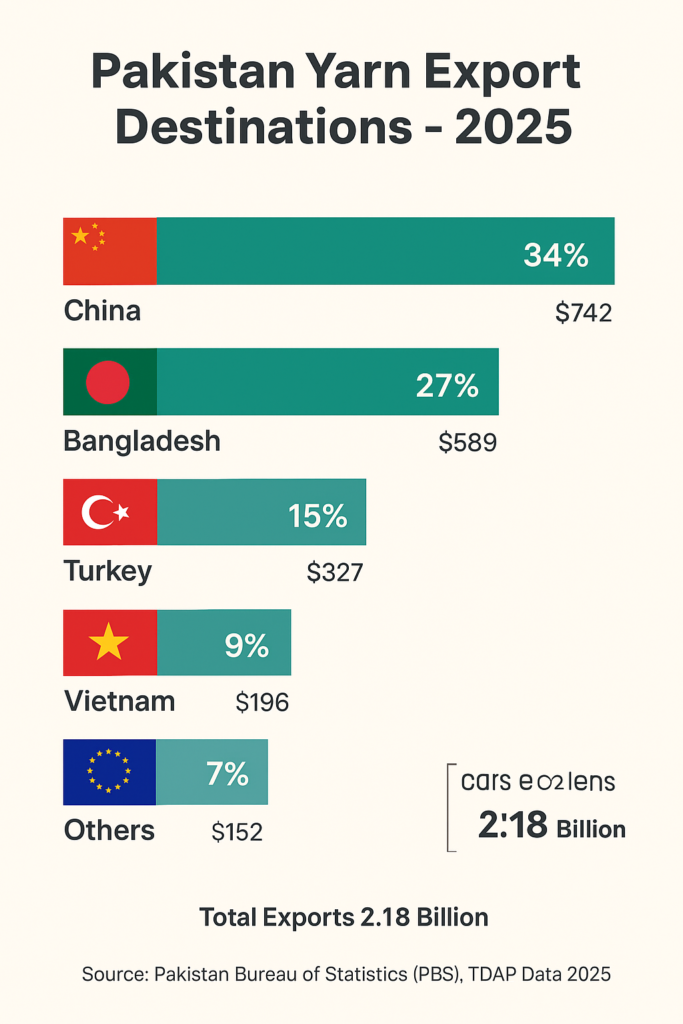
Pakistan is one of the top five manufacturers and exporters of cotton yarn in the world. It sends a lot of yarn to nations like China, Bangladesh, and Turkey. The textile sector is responsible for around 60% of the country’s total export revenues, and yarn is still its most important building element.
However, the yarn market in Pakistan has been going up and down over the past few years because of a number of reasons that are all connected:
- Energy Costs: The up and down prices of electricity and gas are a major factors. This factor makes it more expensive to run spinning machines.
- Currency Depreciation: Although a lower rupee makes exports easier somehow. Yet it also makes it more expensive to buy synthetic fibres and machines.
- Raw Cotton Shortages: U.S. and Brazilian mills face difficulty getting the cotton they need because of floods and unpredictable weather.
- Competition from Regional Players: India and China still own the international market as they are the biggest yarn exporters in the world. This is because they have big economies of scale and better technology.
Pakistan’s textile producers are making their businesses more efficient and able to adapt advanced strategies. Further, Pakistan is also offering a wide range of products, and working on sustainability projects even though these problems exist.
Recent Trends in Pakistan’s Yarn Market (2025):
Although in 2025 Pakistan’s textile producers have already faced challenges, yet they have also faced some opportunities. Meanwhile, there are numerous substantial trends that will have an impact on the market, such as:
Transition to products that provide added value
In order to meet the requirements of premium apparel markets, spinners are placing a greater emphasis on the production of combed, compact, and mélange fibers. In contrast to basic cotton variants, manufacturers can increase their margins and mitigate price volatility by offering superior fibers.
The expansion of synthetic and composite fabric
Pakistani manufacturers invest in polyester-cotton (PC) and viscose-cotton (VC) fiber production. These investments are in response to a growing global demand for composite fabrics. In the Middle East and East Asia, the primary focus on these markets has consistently increased synthetic textile exports.
Putting money into energy efficiency
Many spinning units are using solar energy systems, waste heat recovery, and new machines to lower their manufacturing costs. Energy-efficient operations not only save money, but they also make businesses more competitive when it comes to exports under global environmental requirements.
Sustainability and the capacity to trace things
International purchasers now put a lot of weight on being able to trace where textiles come from. The best spinning groups in Pakistan are working with Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) and Organic Cotton Standards (OCS) certifications to make sure that the cotton they make is good for the environment. This concentration makes the country look even more like a stable provider in the changing global yarn market.
Recovery and diversification of exports
There was a time in 2023–24 when there weren’t enough raw materials and electricity to produce yarn. But somehow in early 2025, Pakistan started to pick up again yarn exports to the next level. On the other hand, exporters are branching out into new markets such as Central Asia, South America and Eastern Europe. Further, these initiatives make them less dependent on older consumers like China and Bangladesh.
Government and Policy Support
The government of Pakistan has taken some initiatives in order to boost the textile and yarn industry.
Some of the most important things that are happening are:
- Lower import duties on synthetic fibers and machinery to encourage diversity.
- Energy Rate Relief for industries who export goods to make them more competitive on price.
- Incentives for modernization that encourage people to buy high-speed spinning machines and automated systems.
- Export Facilitation Schemes make it easier for textile exporters to go through customs.
Also, the Textile Division and the Trade Development Authority of Pakistan (TDAP) are working together to make it easier for people to get into the market and promote Pakistani yarn at trade shows and fairs throughout the world.
Regional Competition and Opportunities:
Although Pakistan has ongoing efforts in order to fortify its position. Yet the regional cotton and yarn market remains extremely competitive.
- China is the world’s largest yarn producer so far. Meanwhile it has recently shifted its emphasis on sustainable and high-end production. But on the other hand, it has created an opportunity for regional exporters to address low-cost supply deficits.
- India continues to be a formidable competitor in the cotton and yarn international market. This is because of its extensive domestic cotton base and integrated textile value chain.
- Bangladesh, which has historically been a textile importer, has initiated a limited yarn production program. However, it continues to rely significantly on Pakistan and India for raw material imports.
- In order to satisfy the demands of global activewear manufacturers, Vietnam and Indonesia are increasing their synthetic textile production capacities.
The opportunity for Pakistan is in specialization and innovation, as it provides niche fibers such as organic cotton, recycled polyester, and performance composites that are in accordance with global fashion and sustainability trends.
Challenges Facing Pakistan’s Yarn Producers:
Although there has been some progress, the sector’s complete potential is still impeded by a number of structural issues:
- Cotton Production Volatility: Cotton crop production in Pakistan remains inconsistent in many aspects. The main causes behind this inconsistency are infestations, water scarcity and inconsistent seed quality.
- Energy Reliability: The unstable power supply is a continuing and dangerous obstacle to rotating units especially in Punjab and Sindh.
- Technology Gap: Many small and medium spinning mills in Pakistan still operate with outdated machinery. Further these machines are reducing their efficiency and the product quality of yarn.
- Global Demand Fluctuations: Yarn demand slows in Europe and the United States, which are critical finished textile markets. This trend has indirectly impacted the cotton and yarn’s international market.
It is necessary for industry stakeholders and government bodies to step ahead in order to guarantee sustainable growth. Moreover financial institutions must move forward and collaborate in order to address these challenges.
Outlook for 2026 and Beyond:
The future of Pakistan’s yarn sector looks cautiously hopeful. Pakistan could start exporting more again because of modernization efforts and the growing worldwide interest in eco-friendly yarns.
Pakistan might become a stronger regional yarn hub serving a wide range of global textile markets if the government keeps supporting policies and the business keeps focusing on quality and innovation.
Final Thoughts:
Rapidly evolving Asia’s economy is changing international yarn markets quickly. It also aims at sustainability and new technologies on the market. Basically this change is a challenge and also an opportunity for Pakistan to grow in this rapidly evolving market.
Pakistan’s textile industry adapts and grows in a good position. On the other hand, it offers a wide range of products and follows Shariah-compliant. Further, modernizing sustainable methods is changing the world quickly.
Pakistan’s yarn makers have a chance to weave a stronger and more robust future. This is because the world is moving forward with supply chains that are ethical and easy-to-follow. This future will balance making money with being responsible.


































